TraceRank: Abnormal Service Localization with Dis-Aggregated End-to-End Tracing Data in Cloud Native Systems

Abstract
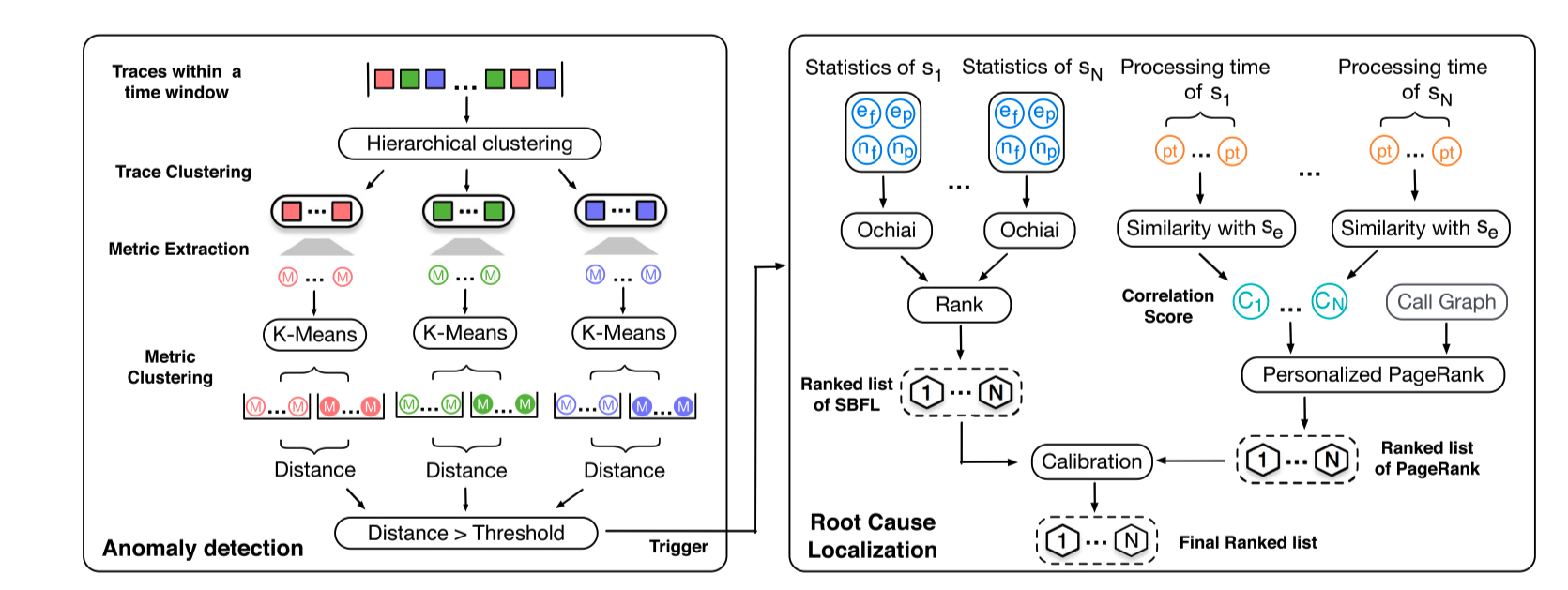
Modern cloud native applications are generally built with a microservice architecture. To tackle various performance problems among a large number of services and machines, an end-to-end tracing tool is always equipped in these systems to track the execution path of every single request. However, it is nontrivial to conduct root cause analysis of anomalies with such a large volume of tracing data. This paper proposes a novel system named TraceRank to identify and locate abnormal services causing performance problems with dis-aggregated end-to-end traces. TraceRank mainly includes an anomaly detection module and a root cause analysis module. The root cause analysis procedure is triggered when an anomaly is detected. To fully leverage the information provided by the tracing data, both the spectrum analysis and the PageRank-based random walk methods are introduced to pinpoint abnormal services. The experiments in TrainTicket and Bookinfo microservice benchmarks and a real-world system show that TraceRank can locate root causes with 90% in Precision and 86% in Recall. TraceRank has up to 10% improvement compared with several state-of-the-art approaches in both Precision and Recall. Finally, TraceRank has good scalability and a low overhead to adapt to large-scale microservice systems.
The blow figure shows the framework of TraceRank.